What is a Head Gasket?
Introduction
The engine is the heart of any vehicle, responsible for converting fuel into the power that propels the vehicle forward. Within this complex system, numerous components work in harmony to ensure smooth and efficient operation. One such critical component is the head gasket. The head gasket plays a pivotal role in maintaining engine performance and reliability, acting as a seal between vital engine parts. Understanding the head gasket’s function and importance is essential for anyone interested in vehicle maintenance or engine mechanics.
Definition of a Head Gasket
A head gasket is a crucial component in an internal combustion engine, positioned between the cylinder head and the engine block. Its primary function is to seal the combustion chamber, preventing the leakage of coolant, oil, and exhaust gases. By maintaining a tight seal, the head gasket ensures that the engine operates under optimal pressure and temperature conditions, thereby enhancing performance and longevity.
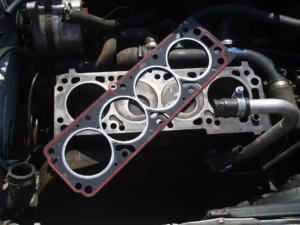

Materials Used for Head Gaskets
Diesel Engines
Diesel engines typically utilize a metal and rubber composite gasket. The metal component provides the necessary strength and heat resistance required to withstand the high-pressure and high-temperature environment of diesel engines. The rubber element offers excellent sealing capabilities, ensuring that fluids do not leak under extreme conditions. This combination is essential for maintaining engine integrity and performance in diesel-powered vehicles, which often operate under more demanding conditions than their gasoline counterparts.
Gasoline Engines
In contrast, gasoline engines, commonly found in passenger vehicles, often use pure rubber head gaskets. The lower pressures and temperatures typical of gasoline engines do not require the additional strength provided by metal components. Pure rubber gaskets are sufficient to handle the sealing needs, offering flexibility and durability without the added weight or complexity of a composite gasket. However, it’s important to note that various engine requirements may necessitate different gasket materials.
Different Combinations and Varieties
Head gaskets come in a variety of types to meet specific engine requirements. Composite gaskets combine multiple materials to achieve desired properties, while multi-layered steel (MLS) gaskets offer enhanced strength and durability for high-performance engines. Pure rubber options are available for engines with lower stress demands. Each design is tailored to meet the unique specifications and performance needs of different engines, ensuring optimal sealing and protection against leaks.
Structure and Design of a Head Gasket
Head gaskets typically feature common design elements such as multi-layered steel and elastomer seals. These components work together to create a precise and robust construction capable of withstanding the intense pressures, temperatures, and chemical exposure found within an engine. The gasket seals the junction between the cylinder head and engine block, preventing leaks and ensuring that the engine operates efficiently. Precise construction is vital, as any imperfections can lead to leaks or failures, compromising engine performance and reliability.
Function of a Head Gasket
The head gasket serves several critical functions within an engine:
- Sealing the Combustion Chamber: It prevents the leakage of coolant, oil, and exhaust gases, ensuring that the combustion process remains contained and efficient.
- Maintaining Proper Pressure and Temperature: By sealing the engine’s internal components, the head gasket helps maintain the necessary pressure and temperature for optimal engine performance.
- Preventing Cross-Contamination: It stops the mixing of engine fluids, such as oil and coolant, which can lead to significant engine damage if not properly managed.
Symptoms of a Failing Head Gasket
A failing head gasket can manifest through various symptoms, signaling potential engine issues:
- Overheating Engine: A common sign of gasket failure, overheating can result from coolant leaks or reduced cooling efficiency.
- Loss of Coolant: Coolant may leak into the combustion chamber or outside the engine, leading to a noticeable drop in coolant levels.
- White Smoke from the Exhaust: This indicates that coolant is entering the engine, where it is burned alongside fuel.
- Engine Misfire or Poor Performance: Loss of compression due to a faulty gasket can cause the engine to misfire or operate inefficiently.
- Contaminated Oil: Coolant mixing with oil can cause the oil to appear milky or foamy, a clear indicator of gasket failure.
Early detection of these symptoms is crucial to prevent severe engine damage and avoid costly repairs.
Consequences of a Blown Head Gasket
If a head gasket fails completely, it can lead to extensive engine damage. Potential consequences include:
- Engine Damage: Warped cylinder heads, cracked engine blocks, or severe engine misalignment can occur, often requiring major repairs or engine replacement.
- High Repair Costs: Fixing a blown head gasket is labor-intensive and costly, especially if additional engine components are damaged.
- Engine Replacement: In severe cases, the extent of the damage may necessitate replacing the entire engine, representing a significant financial burden.
How to Prevent Head Gasket Failure
Preventing head gasket failure involves regular maintenance and proactive care of the engine:
- Regular Maintenance: Consistently checking coolant levels, oil quality, and engine temperature can help identify potential issues early.
- Avoiding Engine Overheating: Ensuring proper coolant circulation and addressing cooling system issues promptly helps prevent overheating.
- Proper Engine Tuning and Inspections: Regular engine tuning and inspections can extend the life of the head gasket by maintaining optimal engine performance and addressing minor issues before they escalate.
Replacement of a Head Gasket
Replacing a head gasket is a complex process that typically requires specialized tools and professional expertise. The procedure involves disassembling parts of the engine to access the gasket, carefully removing the old gasket, and installing a new one with precision to ensure a proper seal. Replacement is necessary in the following scenarios:
- After Overheating: Engine overheating can cause gasket failure, necessitating replacement to restore proper sealing.
- During Regular Maintenance Checks: Proactive replacement during maintenance can prevent unexpected failures.
- If Failure Symptoms Are Present: Addressing symptoms such as coolant loss, white exhaust smoke, or engine misfires promptly can prevent further engine damage.
Conclusion
The head gasket is a vital component in maintaining engine performance and reliability. Its role in sealing the combustion chamber, preventing fluid leaks, and maintaining optimal engine conditions cannot be overstated. Selecting the correct type of gasket material, whether for diesel or gasoline engines, is essential for ensuring engine longevity and performance. Regular maintenance and vigilant monitoring of gasket condition are key to avoiding costly repairs and sustaining the health of your vehicle’s engine.
Contact Information
For any related inquiries or products, please visit drorubber.com.
WhatsApp: +0086 15815831911
WeChat: +0086 13784044874





