Design Considerations and Material Choices for Maintaining Seal Integrity and Preventing Leaks (Including Skeleton Oil Seals)
Introduction
- Overview of the critical role of seals in industrial applications (automotive, manufacturing, construction, etc.).
- Definition of seal integrity and the significant consequences of leaks (equipment failure, safety risks, contamination).
- The objective of the article: Exploring essential design considerations, material choices, and a deeper focus on skeleton oil seals to maintain seal integrity and prevent leaks.
Understanding Seal Integrity
- Key factors that define seal integrity: durability, resistance to pressure, temperature extremes, and chemical exposure.
- Consequences of compromised seal integrity: operational inefficiency, environmental risks, and safety hazards.
- Importance of ensuring seals provide consistent, reliable performance over time.
- Key Design Considerations for Seals
- Seal Geometry
- The importance of choosing the right shape, size, and surface contact area for effective sealing.
- Different types of seals: O-rings, gaskets, lip seals, U-cups, and skeleton oil seals.
- Compression and Stress Distribution
- Ensuring optimal compression to maintain seal effectiveness while avoiding damage to the material.
- Seal Location and Assembly
- How the installation environment impacts seal placement, alignment, and long-term performance.
- Temperature and Pressure Extremes
- Design considerations for seals exposed to fluctuating or extreme temperatures and pressures.
- Environmental Factors
- The influence of external factors like UV rays, moisture, chemicals, and abrasives.
- The difference in design for dynamic versus static seals (moving vs stationary parts).
- Seal Geometry
- Skeleton Oil Seals: Types and Differences
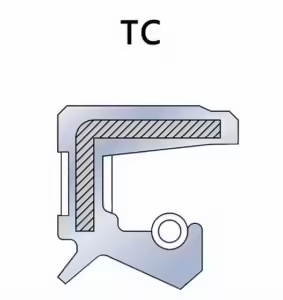
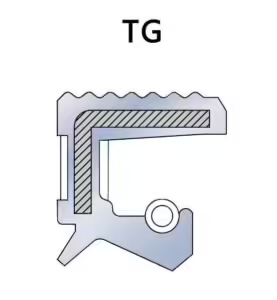
- TC Skeleton Oil Seals
- Commonly used, characterized by a double-lip design: main lip seals the oil, secondary lip prevents dust entry.
- Comparison with TG design: same structure but with a slight difference in the external thread.
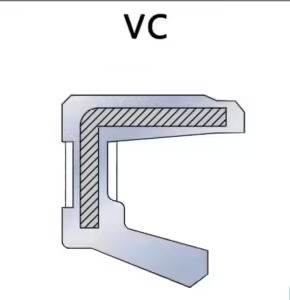
- VC Skeleton Oil Seals
- Single-lip design used for narrow spaces (axis and hole), primarily for dust prevention.
- Main lip does not include a self-tightening spring, making it suitable for simpler applications.
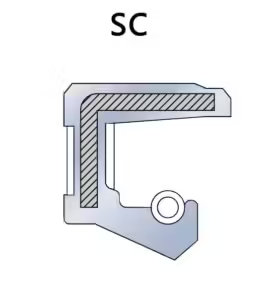
- SC Skeleton Oil Seals
- A variant of TC, with one less dust lip, making it suitable for cleaner environments with minimal dust exposure.
- Typically used where the operating environment is less harsh and where dust is not a primary concern.
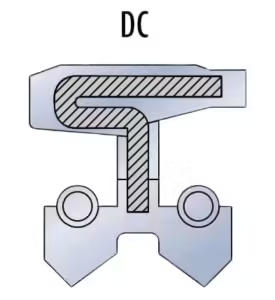
- DC Skeleton Oil Seals
- Designed specifically for dust-prone environments, with a dual lip system (main lip and dust lip), both equipped with sealing springs.
- Ideal for applications exposed to significant amounts of dust and debris.
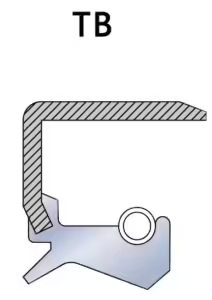
- TB Skeleton Oil Seals
- External skeleton design for better shock resistance and heat dissipation.
- The metal skeleton enhances the seal’s self-tightening ability, durability against vibrations, and provides superior thermal conductivity compared to rubber-based seals.






- TC Skeleton Oil Seals
- Material Selection for Seals
- Elastomers
- Common elastomers used in sealing applications: Nitrile (NBR), EPDM, Silicone, Fluoroelastomers (FKM), etc.
- Key material properties: elasticity, chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, and durability.
- Thermoplastics and Metal Seals
- PTFE and its advantages in chemical resistance and high-performance sealing.
- Metal seals for high-pressure, extreme-temperature, or aggressive environments.
- Hybrid Materials and Coatings
- Combining the benefits of multiple materials for superior performance.
- Coatings that improve wear resistance, chemical resistance, or anti-friction properties.
- Material Selection Criteria
- How to select the ideal material based on specific operational conditions (chemical exposure, temperature, pressure).
- Balancing factors like cost, material availability, and required performance.
- Elastomers
- Challenges in Seal Integrity and Preventing Leaks
- Wear and Aging
- Factors leading to seal degradation: friction, heat, chemical exposure, and more.
- Methods to reduce wear: material selection, surface treatment, and design improvements.
- Chemical and Fluid Compatibility
- The importance of choosing seals resistant to various oils, fuels, chemicals, and other fluids.
- Risk of material breakdown when chemical compatibility is not considered.
- Seal Extrusion and Deformation
- Causes of extrusion: excessive pressure, improper seal geometry, and incorrect material selection.
- Design solutions to mitigate extrusion, such as reinforcement or more resilient materials.
- Wear and Aging
- Testing and Validation of Seal Integrity
- Overview of different testing methods to validate seal performance (pressure testing, leak testing, accelerated aging).
- Importance of pre-installation testing to avoid failures.
- Monitoring seal performance during operation to ensure long-term integrity.
- Conclusion
- Recap of the importance of effective seal design and material selection in preventing leaks and ensuring long-term system reliability.
- Highlighting the role of skeleton oil seals in applications where specialized features are required (e.g., dust resistance, vibration absorption).
- Emphasis on consulting experts and choosing the right seals for specific operational needs to optimize performance.
- Call to Action
- Encourage readers to consult seal experts or reliable suppliers for customized seal solutions.
- Promote Drorubber’s range of high-quality seals, including skeleton oil seals, for diverse industrial applications.
Contact Information:
- Website: drorubber.com
- WhatsApp: +0086 15815831911
- WeChat: +0086 13784044874